How a Water pH Sensor Helps Detect Water Contamination
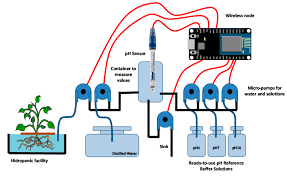
Ensuring water safety is a top priority for municipalities, industries, and private users. Contaminated water poses serious risks to public health, infrastructure, and the environment. Among the indicators used to assess water quality, pH is one of the most critical. It reflects the water’s acidity or alkalinity, which can signal the presence of contaminants or chemical imbalances. Accurate monitoring of pH levels is therefore essential for early detection and prevention of water-related hazards.
A reliable solution for detecting changes in water quality is a water ph sensor. This device provides continuous, real-time monitoring of water’s pH, allowing operators to identify potential contamination quickly. By integrating these sensors into water systems, authorities can respond proactively, minimizing risks and maintaining safe water standards.
Understanding the Importance of pH in Contamination Detection
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 considered neutral. Water with a pH below 7 is acidic, while water above 7 is alkaline. Safe drinking water typically falls within a range of 6.5 to 8.5. Deviations from this range can indicate chemical contamination, the presence of harmful microorganisms, or environmental influences such as industrial runoff.
Regular monitoring of pH is crucial because small changes can serve as early warning signs of contamination. A sudden drop or rise in pH may point to chemical spills, bacterial growth, or other water quality issues that require immediate attention. Continuous monitoring ensures that these changes are detected promptly, preventing further risk to consumers.
How a Water pH Sensor Detects Contamination
Water pH sensors operate by measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions in the water. The sensor converts this chemical activity into an electrical signal, which is then translated into a pH value. Modern sensors are highly sensitive and capable of delivering real-time data under a wide range of conditions.
When integrated into automated monitoring systems, a water pH sensor can continuously log pH levels, trigger alerts if values move outside safe ranges, and even interface with treatment systems for corrective action. This level of automation enhances both accuracy and reliability, making it easier to maintain consistent water quality.
Protecting Public Health
Monitoring pH is a critical part of safeguarding public health. Acidic water can corrode pipes, releasing harmful metals such as lead or copper into the water supply. Alkaline water can compromise the effectiveness of disinfectants, allowing pathogens to persist. By using a water pH sensor, water providers can detect these potentially hazardous conditions early and implement corrective measures before contamination reaches consumers.
Early detection through real-time monitoring also helps prevent waterborne illnesses and ensures that treatment protocols remain effective. Continuous pH measurement is therefore a key component of proactive public health protection.
Enhancing Water Treatment Processes
Water treatment processes rely on precise chemical balances. Disinfectants, coagulants, and other treatment chemicals perform optimally within specific pH ranges. If pH levels shift outside these ranges, treatment efficiency declines, increasing the risk of contamination.
A water pH sensor provides accurate, continuous feedback, allowing operators to adjust chemical dosing and treatment procedures in real time. This ensures that water treatment is both efficient and effective, reducing chemical waste and maintaining high water quality standards.
Applications Across Multiple Sectors
While municipal water systems are the primary users of pH sensors, these devices are also valuable in industrial, agricultural, and environmental applications. Industrial facilities monitor pH to ensure process consistency and compliance with environmental regulations. Agricultural operations track irrigation water to protect soil health and crop productivity. Aquaculture facilities use pH sensors to maintain stable aquatic environments.
In all these cases, real-time pH monitoring enables early detection of potential contamination, supporting operational efficiency and safety.
Supporting Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory bodies require accurate, ongoing monitoring of water quality, including pH levels. Continuous monitoring using a water pH sensor simplifies compliance by providing reliable, automatically recorded data. This reduces the likelihood of errors associated with manual testing and ensures a clear record for audits and reporting.
Reliable pH monitoring also builds confidence among stakeholders and consumers, demonstrating that water systems are actively managed to prevent contamination and maintain safety.
Conclusion
Detecting water contamination quickly is essential for health, safety, and operational efficiency. A water pH sensor provides real-time, accurate measurements that allow operators to identify changes in water chemistry early. From protecting public health to optimizing treatment processes and supporting regulatory compliance, these sensors are an indispensable tool in modern water quality monitoring. Continuous pH monitoring ensures that water remains safe, reliable, and fit for consumption across all applications.



